In one of the Earlier Article, we saw how to create an Azure Virtual Machine from the Azure Subscription. As a continuation, let us see, how to host a ASP.Net Application on that VM and access it from the Internet.
The basic steps are as follows.
1. Create the VM – Refer the Article
2. Assign a Public IP to it on the Azure Portal.
3. Purchase a Domain Name.
4. Assign the domain Name to the VM which we created.
5. Add the Network Security Group IPs.
6. Configure the IIS
7. Host the APP with HTTPS.
8. Access it from the internet.
Let us see, the above steps in detail.
1. Create the VM – Already we saw this.
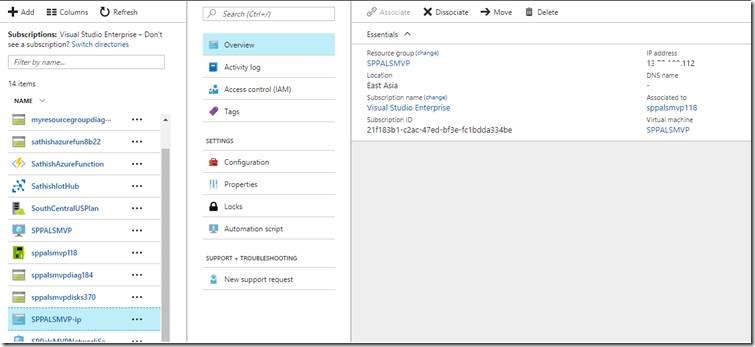
2. Assign a Public IP to the VM
a. Login to the Azure Portal
b. As soon as you create a new VM, a set or resource groups will be created.
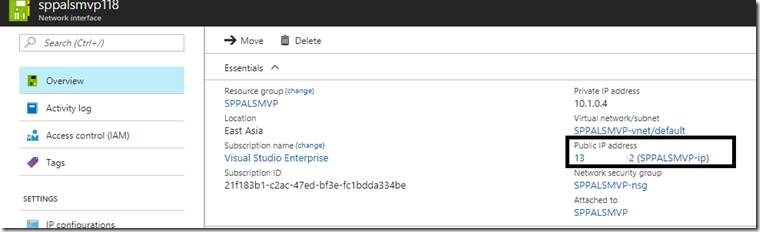
c. Select the Network Interface from the “All Resources”
d. The Properties screen will be as below.
e. Make sure that, the same IP is Associated with the VM.
3. Purchase the domain name.
a. We can purchase the domain from any vendor. In my case, I used namecheap.com.
4. Assign that domain to the VM. This is a separate topic, let us discuss about this in future articles.
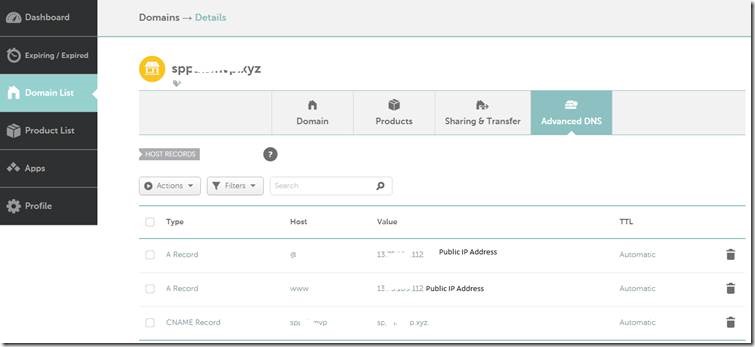
5. In the Namecheap.com, add the IP Address (the public IP, which we mentioned on the above steps) as the DNS Entries.
6. Wait for a day. This DNS entries will not be reflected immediately.
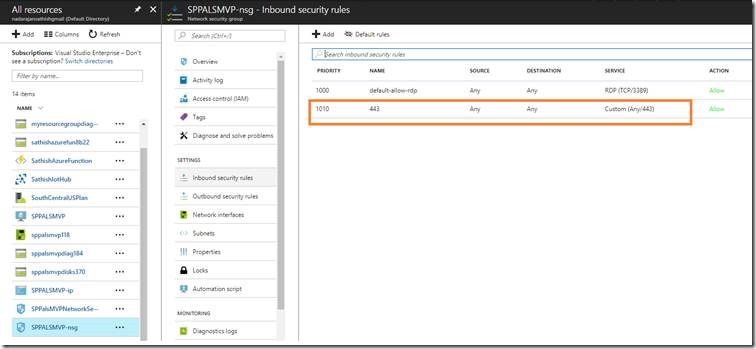
7. Add the Network Security Group – Inbound Security Rules in the Azure VM
a. By default, the RDP entry will be there. We need to Add one more entry for the 443 port. (In which, we are going to host our ASP.Net web site)
8. Now, on the IIS, let us create a Web Application. It is always better to use the Default Web Site and create the Virtual Directories under that main web site.
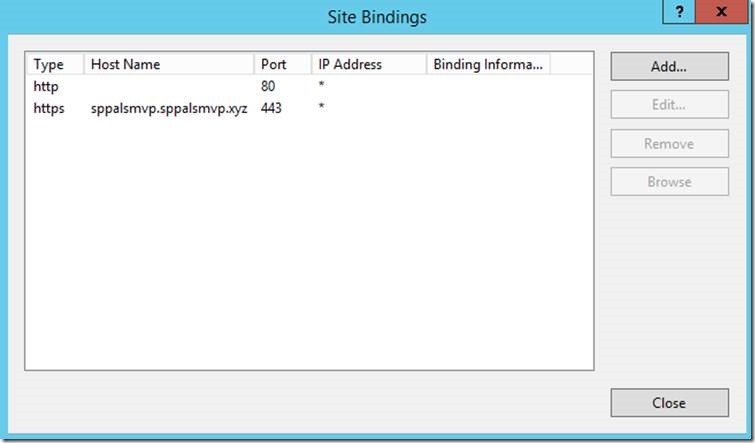
9. Make sure that, we have a proper Certificate and a binding as below.
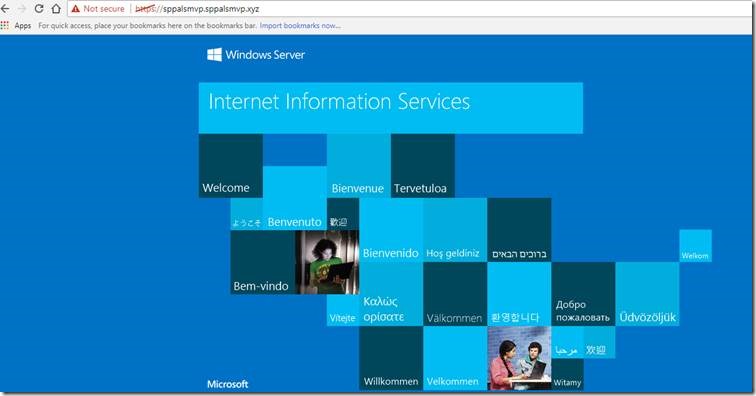
10. Now, try accessing the site using the url https://sppalsmvp.sppalsmvp.xyz.
11. The site loads as below.
Happy Coding,
Sathish Nadarajan.


Leave a comment